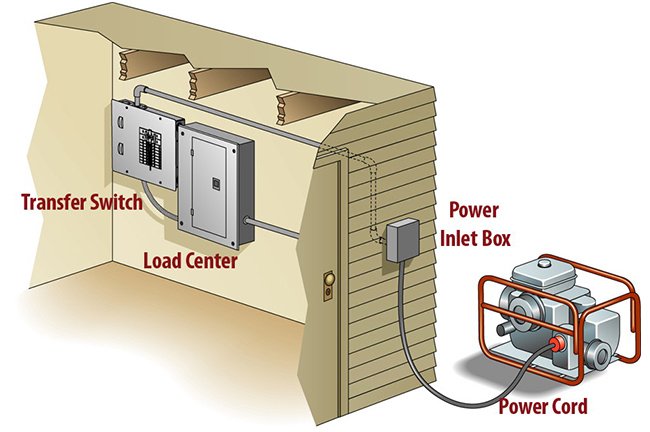
Power outages can feel like a sudden return to the dark ages, disrupting everything from your morning coffee to critical medical devices. But with the right backup power system, you can keep the lights on, the fridge cold, and your essential electronics humming. The unsung hero of this seamless transition? The transfer switch.
When it comes to Choosing the Right Transfer Switch for Your Home backup power, it's not just about convenience; it's about safety and protecting your home's electrical system. This guide will help you confidently navigate the options, ensuring you pick a system that’s perfect for your needs, your budget, and your peace of mind.
At a Glance: Your Transfer Switch Essentials
- Safety First: A transfer switch is non-negotiable for generator use; it prevents dangerous "backfeeding" into the utility grid.
- Two Main Types: Choose between Manual (cost-effective, hands-on) or Automatic (convenient, seamless, higher cost).
- Calculate Your Needs: Determine your essential wattage, then add a 20-25% buffer for starting surges.
- Circuits Matter: Decide how many appliances or areas absolutely need backup power (e.g., 6 for essentials, 12+ for whole home).
- Check Compatibility: Ensure your switch matches your generator's voltage, phase, and connection type.
- Pro Installation is Key: While some basic manual switches might seem DIY-friendly, professional installation is crucial for safety and code compliance.
- Look for Certifications: UL 1008, ETL, and NEMA ratings guarantee safety and performance.
Why a Transfer Switch Isn't Optional (It's Essential Safety)
Imagine a sudden blackout. You haul out your trusty generator, fire it up, and plug it directly into a wall outlet. Sounds simple, right? Wrong. This common, dangerous practice is called "backfeeding," and it can have catastrophic consequences.
A transfer switch acts as a crucial electrical gatekeeper. It safely transfers your home's power source between the utility grid and your backup generator. Without it, your generator's power could flow backward into the utility lines, potentially electrocuting utility workers trying to restore power, or causing significant damage to your home's electrical system. It's not just a recommendation; it's often a legal requirement by electrical codes to ensure the safety of your household and utility personnel.
Manual vs. Automatic: Which Power Play Is Right For You?
The first big decision you'll face is choosing between a manual and an automatic transfer switch. Each has distinct advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different scenarios and budgets.
Manual Transfer Switches: Hands-On Reliability
As the name suggests, a manual transfer switch requires you to physically intervene to switch your home's power source. When the utility power goes out, you'll need to go to the switch, flip a lever or throw a breaker, and then start your generator. Once utility power is restored, you reverse the process.
Pros:
- Cost-Effective: Generally the most budget-friendly option, making them attractive for those with occasional power needs.
- Simplicity: Fewer complex electronic components means less to potentially go wrong.
- Direct Control: You decide exactly when to engage your backup power.
- Easy Installation (relatively): While still requiring professional expertise, the wiring for manual switches can be less intricate than automatic ones.
Cons: - Active Intervention Required: You must be home and awake to operate it. This can be inconvenient, especially during nighttime outages or if you're away.
- Brief Power Interruption: There's a short period of darkness between switching off utility power and engaging the generator.
- Limited Convenience: No automatic testing or monitoring features.
Ideal For: - Smaller homes or cabins.
- Homeowners who experience less frequent or shorter power outages.
- Those on a tighter budget who don't mind a bit of hands-on management.
- Situations where maintaining power to all circuits isn't critical, just a select few essentials.
Automatic Transfer Switches: Seamless, Set-It-and-Forget-It Power
Automatic transfer switches (ATS) are the ultimate in convenience. They constantly monitor the utility power. The moment an outage is detected, the ATS automatically disconnects your home from the utility grid, signals your generator to start, and then transfers power to the generator. All of this happens within seconds, often without you even noticing a flicker. When utility power returns, the ATS reverses the process, shutting down the generator after a cool-down period.
Pros:
- Seamless Operation: Power transfers automatically, whether you're home or not.
- Uninterrupted Power: Ideal for critical systems like medical equipment, security systems, or sensitive electronics that can't tolerate even a brief power loss.
- Enhanced Safety: Eliminates the risk of human error during power transfer.
- Convenience: No need to go outside in bad weather or wake up in the middle of the night.
- System Integration: Many modern ATS units offer features like remote monitoring, smart home integration, and automatic exercise routines for your generator.
Cons: - Higher Cost: Automatic transfer switches are significantly more expensive than manual models.
- Complex Installation: Involves more intricate wiring and electrical work, almost always requiring professional installation.
- Generator Compatibility: Requires a generator designed for automatic starting and stopping.
Ideal For: - Homes with critical medical equipment or occupants who are sensitive to power interruptions.
- Owners of larger homes or those needing whole-house backup.
- Homeowners who want maximum convenience and peace of mind.
- Anyone who travels frequently and wants their home protected even when they're away.
Decoding Your Needs: Key Factors to Consider
Once you've considered manual versus automatic, it's time to drill down into the specifics. Making the right choice means carefully evaluating several factors related to your home, your generator, and your power habits.
1. Power Capacity: Sizing Up Your Surge Power
This is perhaps the most critical factor. Your transfer switch must be rated to handle the total electrical load of everything you plan to power with your generator. Choosing a switch that's too small will lead to overloads and tripped breakers, while one that's too large could mean wasted money.
- Calculate Your Essentials: Make a list of every appliance, light, and electronic device you want to run during an outage. Look at their wattage ratings (usually found on a label on the appliance).
- Account for Starting Surges: Motorized appliances (refrigerators, freezers, well pumps, AC units) draw significantly more power for a few seconds when they first start up. This "starting wattage" can be 2-3 times their running wattage. Your transfer switch (and generator) must be able to handle these momentary surges.
- Add a Buffer: As a rule of thumb, choose a transfer switch rated at least 20-25% above your maximum calculated load (including starting surges). This accommodates unexpected loads and future expansion.
- Common Capacities: Transfer switches are typically rated in Amps (A) and Watts (W).
- 30A (7,500W): Sufficient for basic essentials in a small home, often paired with Understanding portable generator switches.
- 50A (12,500W): Good for more comprehensive essential circuits or smaller whole-home applications.
- 100A (24,000W) - 200A (48,000W): Standard for larger homes requiring whole-house backup, especially with larger standby generators.
2. How Many Circuits Do You Need to Keep On?
Do you just need to keep the fridge and a few lights on, or do you want your entire home to function as normal? The number of circuits your transfer switch can accommodate directly impacts what parts of your home receive backup power.
- Essential Circuits: For basic needs, 6-10 circuits are usually enough. These might include your refrigerator, furnace fan, a few lights, a microwave, and a couple of outlets for charging devices.
- More Critical Systems/Larger Homes: For more comprehensive backup or larger homes, 12 circuits or more might be necessary. This could extend to well pumps, water heaters, security systems, and more general-purpose outlets.
- Whole-Home Solutions: For whole-home backup, particularly with an automatic standby generator, you'd typically opt for a 100A or 200A automatic transfer switch that manages all circuits in your main electrical panel.
3. Compatibility is Key: Matching Your Generator and Home
Your transfer switch isn't a standalone component; it's a bridge between your generator and your home's electrical system. Ensuring compatibility is non-negotiable.
- Voltage: Most residential homes in the US use 120/240V. Your generator and transfer switch must match this.
- Phase: Residential homes are single-phase. Ensure your generator and transfer switch are also single-phase.
- Connection Type: This refers to the specific plug and receptacle your generator uses (e.g., L14-30R for 30A, L14-50R for 50A). The transfer switch's inlet box must be compatible.
4. Location, Location, Location: Indoor vs. Outdoor Considerations
Where will your transfer switch be installed? This determines the necessary weatherproofing and enclosure ratings.
- Indoor Switches: Designed for protected environments like basements, garages, or utility rooms. They don't require special weather resistance.
- Outdoor Switches: Crucial if your electrical panel or generator connection point is outside. Look for:
- NEMA 3R or higher weatherproof ratings: This signifies protection against rain, sleet, snow, and external ice formation.
- Corrosion-resistant materials: Galvanized steel, aluminum, or special powder coatings help withstand the elements.
- Sealed covers and gaskets: To prevent moisture intrusion.
- GenerLink, for example, is specifically designed for outdoor installation, connecting directly behind your electric meter.
5. Safety First: Certifications You Can Trust
Electrical work carries inherent risks. To ensure your transfer switch meets stringent safety and performance standards, always look for specific certifications.
- UL 1008: This is the most important certification for transfer switches in the US, indicating compliance with Underwriters Laboratories' safety standards for automatic transfer switches.
- ETL Listed: Similar to UL, this means the product has been tested and meets applicable safety standards by Intertek.
- NEMA Standards: National Electrical Manufacturers Association standards define performance and environmental specifications for enclosures. A NEMA 3R rating, as mentioned, is crucial for outdoor units.
6. Installation: DIY or Pro?
Wiring a transfer switch involves dealing with high voltage and intricate connections.
- Professional Installation Recommended: For most homeowners, especially for automatic or high-capacity systems, hiring a licensed electrician is not just recommended, it's essential. They ensure the installation is safe, up to code, and correctly integrated with your home's electrical system.
- DIY for Experts Only: If you are a certified electrician or have extensive experience with residential wiring and local codes, a simple manual transfer switch might be a DIY project. However, the risks of shock, fire, and improper function are extremely high for the untrained. Don't take chances with your home and family's safety.
7. Built to Last: Durability and Weatherproofing
A transfer switch is a long-term investment. You want one that can reliably perform when needed, often under duress.
- Material Quality: Look for robust construction, often with steel cabinets (like the A510C Pro/Tran2).
- Contact Points: High-quality switches have durable contacts that can withstand frequent switching and high electrical loads without excessive wear.
- Weatherproofing: If installed outdoors, reiterating the need for NEMA 3R+ ratings, corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., galvanized steel), waterproof covers, and sealed wiring entry points is critical. Connecticut Electric's EmerGen Kits, for instance, are NEMA 3R rated.
8. The Bottom Line: Cost and Your Budget
Your budget will naturally play a significant role in your decision.
- Manual Transfer Switches: Prices can range from approximately $50 for basic models (e.g., small, limited circuit switches) to $300-$600 for more robust units with multiple circuits and higher amperage.
- Automatic Transfer Switches: Expect to pay anywhere from $500 to over $1,500 for the unit itself, depending on capacity, features, and brand.
- Installation Costs: Don't forget to factor in professional installation. This can add several hundred to over a thousand dollars, depending on the complexity of the job, your home's existing wiring, and local labor rates. A complex automatic transfer switch installation integrated with a whole-house standby generator could run into the thousands.
Common Pitfalls: Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Transfer Switch
Making an informed decision means also being aware of the missteps others have made. Avoid these common mistakes:
- Choosing the Wrong Power Capacity: Under-sizing leads to frustrating overloads and a generator that can't power your essentials. Over-sizing wastes money. Always calculate your needs precisely and add that 20-25% buffer.
- Ignoring Compatibility Issues: A 30A generator won't work with a 50A transfer switch inlet, nor will a single-phase home accept a three-phase switch. Double-check voltage, phase, and connection types between your generator, home, and switch.
- Overlooking Essential Safety Features: Don't skimp on safety. Ensure your chosen switch has appropriate UL/ETL certifications and includes features like automatic shutoff (in ATS) or a lockout mechanism (in manual switches) to prevent simultaneous connection to utility and generator power.
- Improper Installation (or DIY if Not Qualified): This is perhaps the most dangerous mistake. An improperly installed transfer switch risks electrical shock, fire, equipment damage, and serious code violations. Always use a qualified, licensed electrician.
- Not Considering Future Needs: Thinking you'll only need a few circuits now, but potentially expanding your generator setup or adding more essential appliances later? Choose a switch that allows a bit of room to grow to avoid costly upgrades down the line.
Beyond the Install: Maintenance and Modern Features
Once your transfer switch is installed, it's easy to forget about it – until you need it. A little proactive care goes a long way.
- Regular Inspections: Every few months, visually inspect your transfer switch. Look for signs of corrosion, loose connections, or debris (especially for outdoor units).
- Monthly Operational Testing: Most manufacturers recommend exercising your generator and testing your transfer switch monthly. For automatic systems, this can often be scheduled to run automatically. For manual systems, initiate a test transfer to ensure everything is working correctly.
- Annual Professional Inspections: Have a qualified electrician inspect your transfer switch annually. They can check for wear on contacts, verify proper voltage, and ensure all connections are secure.
Smart Home Integration: Modern transfer switches, particularly automatic models, are increasingly offering smart features. Look for models that can integrate with smart home systems via Wi-Fi or Z-Wave. This can provide: - Remote Monitoring: Check generator status, fuel levels, and transfer switch activity from your smartphone.
- Remote Control: Some systems allow you to remotely start/stop your generator or initiate test runs.
- Alerts and Notifications: Receive instant alerts about power outages, generator errors, or maintenance reminders.
Trusted Brands and What They Offer
The market offers a variety of reputable brands, each with their own strengths:
- Generac: A leader in the generator market, Generac offers robust automatic transfer switches. Their 200 Amp Single Phase ATS units, often featuring Digital Power Management and UL listing, are a popular choice for whole-home standby generators, typically backed by a 5-year warranty.
- Reliance Controls: Known for a wide range of manual transfer switches and power inlet boxes. Models like the 306CRK support up to 6 circuits and 7500W, often coming pre-wired for a somewhat easier (though still professional) installation.
- Connecticut Electric: Provides reliable manual options such as the Series 2 (50 Amps, 12,500W, 10 circuits, with a weather-resistant inlet box) and their convenient EmerGen Kits (supporting up to 10 circuits for 30A generators, NEMA 3R rated).
- Nature’s Generator: For those exploring portable or hybrid power solutions, Nature’s Generator offers indoor, 12-circuit (12,000W) UL-certified transfer switches designed to integrate with their own power systems.
- A510C Pro/Tran2: A popular choice for manual operation, this 50-Amp, 10-circuit manual switch is UL 1008 listed and housed in a durable steel cabinet.
- GenerLink: Offers a unique automatic transfer switch solution that installs directly behind your electric meter, ideal for portable generators under 8,500 watts and up to 200 AMP service. It comes with a 20-foot power cable and weatherproof housing for convenience.
Your Next Steps: Making an Informed Decision
Choosing the right transfer switch for your home's backup power isn't a decision to take lightly. It impacts your safety, convenience, and investment.
- Assess Your Power Needs: Start by making that crucial list of essential appliances and calculating your required wattage, including surge capacity.
- Determine Your Preferred Automation Level: Decide if a manual system fits your lifestyle and budget, or if the convenience and seamlessness of an automatic switch are worth the extra investment.
- Check Compatibility: Ensure your chosen switch aligns with your existing or planned generator and your home's electrical system specifications.
- Consult a Professional: Always, always involve a licensed electrician. They can help verify your calculations, advise on the best type of switch for your specific setup, ensure code compliance, and perform a safe, reliable installation. Their expertise is invaluable in protecting your home and family.
With a well-chosen and professionally installed transfer switch, you can face the next power outage not with dread, but with confidence, knowing your home will remain powered and your family safe.